The textile industry encompasses a vast array of manufacturing processes, each contributing unique properties to the final fabric. Among these, weaving and knitting stand out as two fundamental techniques, resulting in distinct textile characteristics that influence their diverse applications. Understanding the core differences between these methods is crucial for professionals across various sectors, from fashion and apparel to industrial and technical textiles.
Weaving: Interlacing for Stability
Weaving is an age-old technique that involves interlacing two sets of yarns, known as the warp and the weft. The warp yarns run lengthwise on the loom, while the weft yarns are inserted perpendicularly across the warp. This perpendicular interlacement creates a stable and rigid structure.
Process: The weaving process is executed on a loom, which holds the warp yarns under tension. A shuttle or other insertion device carries the weft yarn across the warp, creating the interlaced pattern. Different weaving patterns, such as plain weave, twill weave, and satin weave, result in varied fabric textures and properties.
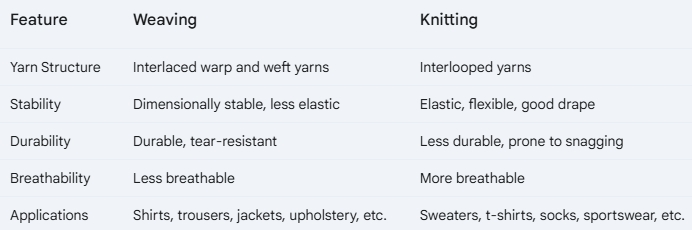
Characteristics: Woven fabrics are generally dimensionally stable, meaning they resist stretching and deformation. They are also known for their durability and resistance to tearing. However, they tend to be less elastic compared to knitted fabrics.
Applications: Due to their stability and durability, woven fabrics are widely used in apparel such as shirts, trousers, and jackets. They are also prevalent in home furnishings, upholstery, and industrial applications like canvas and tarpaulins.
Knitting: Interlooping for Flexibility
Knitting, on the other hand, involves interlooping yarns to create a fabric structure. Loops of yarn are interconnected, forming a network of interconnected stitches.
Process: Knitting can be performed by hand or on machines using needles or other loop-forming elements. There are two main types of knitting: weft knitting and warp knitting. In weft knitting, loops are formed horizontally, while in warp knitting, loops are formed vertically.
Characteristics: Knitted fabrics are known for their elasticity, flexibility, and drape. The looped structure allows for significant stretch and recovery. They also tend to be more breathable and comfortable against the skin. However, they are generally less durable and more prone to snagging compared to woven fabrics.
Applications: The inherent elasticity and comfort of knitted fabrics make them ideal for apparel such as sweaters, t-shirts, socks, and sportswear. They are also used in various other applications, including hosiery, medical textiles, and automotive interiors.
Key Differences Summarized
Conclusion
Weaving and knitting are distinct textile manufacturing processes that produce fabrics with contrasting characteristics. Weaving offers stability, durability, and rigidity, while knitting provides elasticity, flexibility, and comfort. The choice between woven and knitted fabrics depends on the specific requirements of the end product. As textile technology continues to advance, both weaving and knitting techniques are constantly evolving, leading to innovative fabrics with enhanced performance and functionality. This understanding of the fundamental differences remains vital for informed decision-making across the textile industry.